Where Does It Change From Central To Eastern Time?
Here is a footling puzzle for you. Y'all are in Moscow and need to phone call your friend in Yakutsk: How many hours practice you lot need to add together or decrease so that you lot don't wake them up at four in the forenoon?
The world is divided into 24 time zones, and Russia covers 11 of them. This is the most time zones in any land (not counting overseas territories). When the due east of Russia is in the middle of the working day, the western regions are nevertheless fast comatose. The closest runners upwardly for the virtually time zones in one country are the United states of america and Canada, which both have six.
St. petersburg time and time zones
But imagine that a mere 150 years ago the earth had no time zones at all. Cities established their own so-called "local solar times," whereby midday came when the sun reached its zenith. The advent of railroads is what created the need to accurately synchronize time with other localities, and time zones were introduced, first in the United Kingdom, the U.S.
In the Russian Empire, the railroads used St. Petersburg time for all schedules. Officially, Russian federation joined the international arrangement of fourth dimension zones only afterward the Bolshevik Revolution. In 1919, the country was divided into 11 time zones with boundaries that went along railroads and rivers. Subsequently, time zone boundaries in Russia were revised on multiple occasions in attempts to bring them into line with regions' authoritative borders.
But if you lot thought the whole time zones saga ended with the collapse of the Soviet Marriage, think again. In 2009, Russia decided to reduce its number of fourth dimension zones from 11 to 9, but then in
Wintertimeforever?
In 1917, Russia for the commencement time switched to
For l years, the Soviet Union lived past that time until it was decided again in 1981 to start switching to summer time and dorsum.
In 2011, the regime responded to complaints from the many Russians who constitute information technology difficult to adjust to changing the clocks twice a year (some fifty-fifty argued that it adversely affected their health), and the practice was abased in one case once again. Every bit a result, some regions ended up with a time that was an hour or sometimes even two hours ahead of their geographic time! Yet, it turned out that the wrong time –
The regime was bombarded with complaints from people who were unable to function normally during what they described equally an actress long and dark Russian wintertime. Finally, in 2014 the authorities ruled that clocks would get dorsum an hr and remain there. Then it is that, for five years at present, Russian federation has been living permanently in
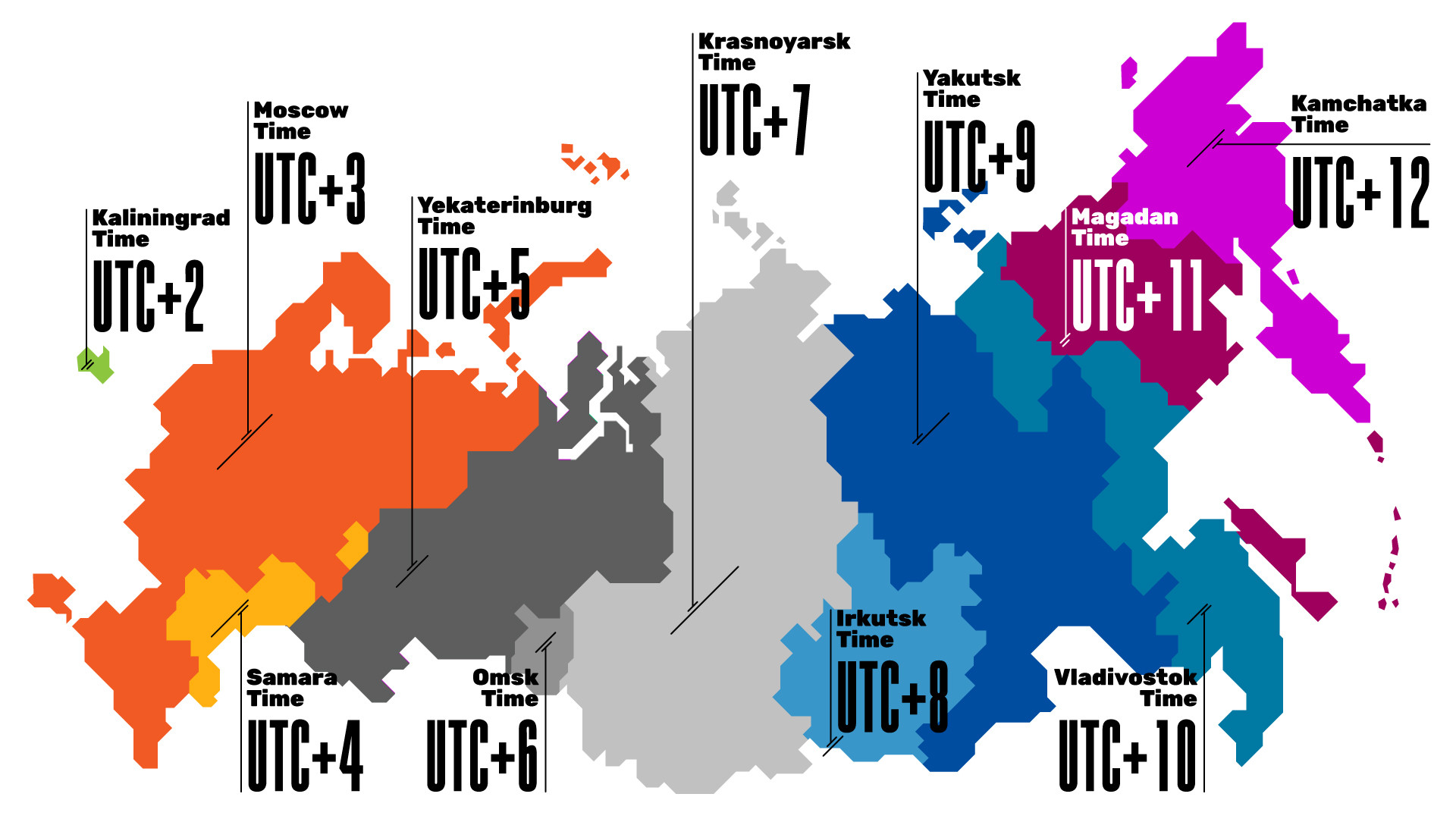
What time zones are there in Russian federation?
Alexander Kislov, Natalya Nosova
2. Moscow fourth dimension (MSK) (UTC+3) covers Moscow and the European part of Russia.
3. Samara time (SAMT) (UTC+iv) covers Astrakhan, Samara, Ulyanovsk and the Saratov regions, likewise as the Udmurt Republic.
4. Yekaterinburg fourth dimension (YEKT) (UTC+5) covers Bashkortostan, the Perm Territory, Kurgan, Orenburg, Sverdlovsk, Tyumen and Chelyabinsk regions, also as the Khanty-Mansi and the Yamal-Nenets autonomous areas.
5. Omsk fourth dimension (OMST) (UTC+6) covers
6. Krasnoyarsk
7. Irkutsk fourth dimension (IRKT) (UTC+8) covers Buryatia and the Irkutsk Region.
8. Yakutsk fourth dimension (YAKT) (UTC+9) covers western Yakutia, Transbaikal Territory
9. Vladivostok time (VLAT) (UTC+10) covers central Yakutia and the Maritime (Primorsky) Territory.
ten. Magadan time (MAGT) (UTC+11) covers eastern Yakutia, as well as the Magadan and Sakhalin regions.
11. Kamchatka (PETT) (UTC+12) covers Kamchatka Territory and the Chukotka democratic area. The time difference with Moscow is 9 hours.
If using any of Russia Beyond's content, partly or in full, e'er provide an active hyperlink to the original material.
Get the calendar week's best stories straight to your inbox
Source: https://www.rbth.com/travel/329966-times-zones-russia
Posted by: spragueyoudiven.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Where Does It Change From Central To Eastern Time?"
Post a Comment